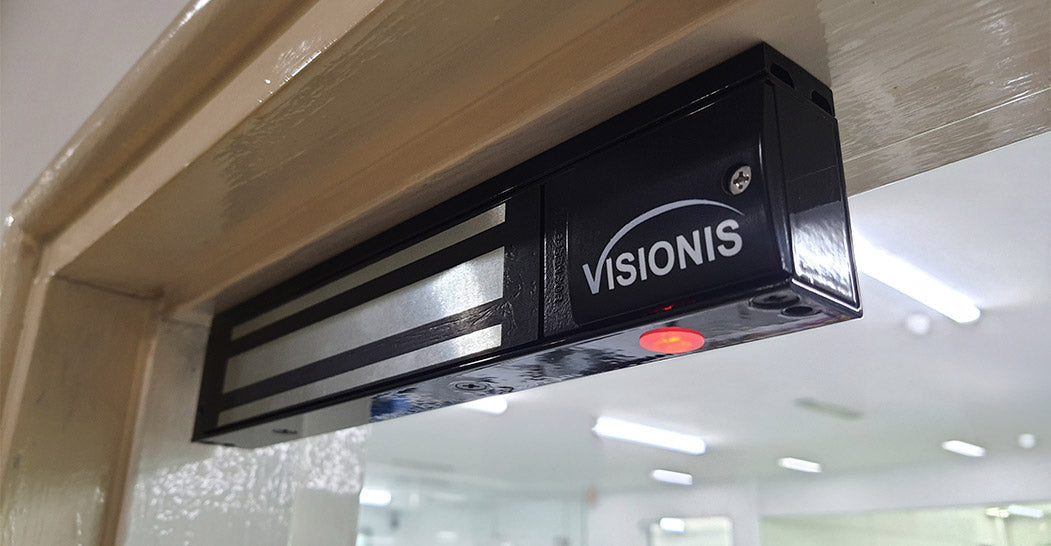
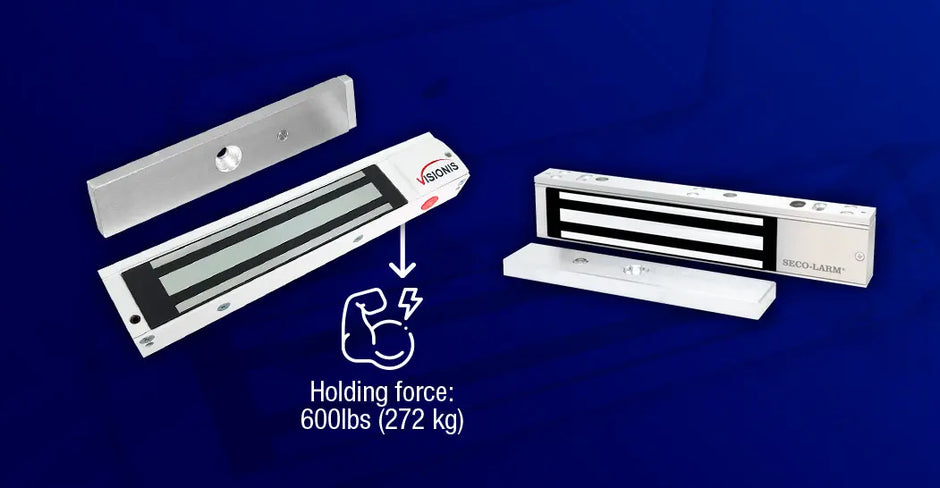
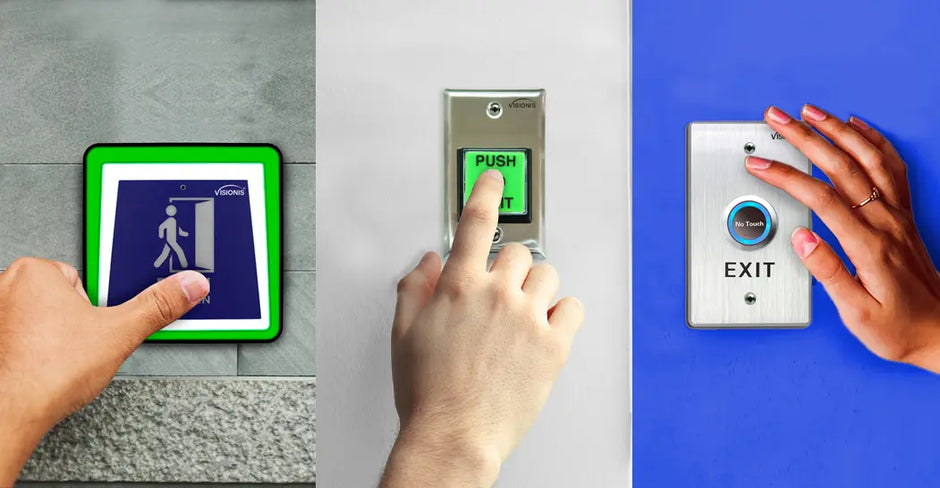
Electromagnetic locks, or maglocks, are a go-to solution for keeping doors secure in homes, offices, and commercial buildings. But how exactly do they work? And why might they be the right choice for you?
If you’ve ever had these questions, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know. From how they operate to installation tips and common concerns, we’ve got you covered.
What are Magnetic Locks?
Think of an electromagnetic lock as the perfect blend of science and security. At its core, a maglock is a device that uses electromagnetism to keep doors locked. It has two main parts:
Electromagnet: This is mounted on the door frame.
Armature Plate: This is attached to the door.

How Do Magnetic Locks Work?
When you supply power to the lock (often through a 12V power source), the electromagnet generates a magnetic field strong enough to hold the armature plate in place. No bolts or moving parts—just pure magnetic force!
If the power is cut, the magnet releases, and the door unlocks. This fail-safe mechanism prioritizes safety, which is especially important for emergency exits.

This simple yet effective design makes electromagnetic door locks perfect for high-traffic areas or situations where quick access control is essential. Plus, many maglocks are compatible with advanced technologies like keycards, biometric scanners, and remote monitoring.
Types of Magnetic Locks

Surface-Mount Maglocks
These are installed on the surface of the door frame and door, making them visible and relatively straightforward to install. They are commonly used in various applications due to their ease of installation and maintenance.
Concealed (or Shear) Locks
These locks are embedded within the door and frame, rendering them invisible when the door is closed.
Not sure which one fits your needs? Reach out to us, and we’ll help you choose the perfect lock for your setup.
Magnetic Lock Door Installation
If you’re thinking of installing a maglock, check out this video. It’s perfect for walking you through the setup step by step.
Types of Brackets for Maglocks
Brackets play a crucial role in ensuring your maglock is securely installed and functioning properly. The type of bracket you need depends on the door and frame setup.
Here are the most common types and when to use them:
L-Bracket
For when the door frame is narrow and for outswing door.

ZL-Bracket
Ideal for inward-opening doors, this bracket helps mount the armature plate to align with the electromagnet.

U-Bracket
Specially made for glass doors, this bracket allows installation without drilling into the glass.

I Bracket for Armature Plate
This is helpful when the door leaf is too thick for screws.

Using the right bracket ensures proper alignment and maximum holding force, keeping your maglock secure and reliable.
Do Magnetic Locks Work Without Power?
Short answer: No.
Electromagnetic door locks don’t work without power. That’s why backup systems are essential. Options include:

Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): Keeps your locks functional for extended periods.
Battery Backup: Provides a short-term power source during outages.
With a backup system in place, you can rest easy knowing your security won’t be compromised.
Regular Maintenance: What You Need to Know
Maglocks are low-maintenance, but regular care and attention are essential for optimal performance:
- Clean the magnet and plate regularly to remove dust and debris.
- Check the alignment between the electromagnet and armature plate.
- Test the lock periodically to ensure it’s functioning properly.
Maglocks require maintenance every 6 to 12 months to ensure they remain in optimal working condition.
Cost and Budgeting for Maglocks
When considering a maglock, it’s essential to factor in both upfront and ongoing costs. Here’s what to keep in mind:
Initial Costs
The price of magnetic locks for door varies based on type and features. Standard surface-mount models are budget-friendly, while specialized options like weatherproof or shear locks may cost more.
Installation
DIY installations save money, but professional setups might be worth it for complex systems.
Maintenance
Regular cleaning and inspections are low-cost but necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Accessories
Don’t forget to account for additional components like push-to-exit buttons, power supplies, and access control devices. Investing in a quality maglock ensures long-term security and peace of mind.
Common Troubleshooting Issues
Even the most reliable magnetic locks can encounter issues. Here are some common problems and their solutions:

Misalignment Between Magnet and Plate
If the door doesn’t lock securely, check and adjust the alignment of the electromagnet and armature plate.
Wiring Errors
Ensure all connections follow the wiring diagram. Loose or incorrect wiring can disrupt functionality.
Power Supply Issues
Verify the power source is providing the correct voltage (typically 12V). A multimeter can help troubleshoot power problems.
Unresponsive Lock
If the lock isn’t engaging, test the control panel or access system to ensure signals are being sent correctly.
Noise or Vibrations
Tighten loose screws or check for debris between the lock and plate to eliminate rattling sounds.

Got a maglock from FPC Security and running into issues? Don’t worry—remember, our expert team is always here to help you out!
Compliance with Building Codes
Before installing door magnetic locks, ensure compliance with local building and fire safety codes. Key considerations include:
Emergency Exits: Maglocks must be released during power outages or fire alarms for safe evacuation.
Push-to-Exit Buttons: Install in accessible locations to meet safety standards.
Professional Consultation: Engaging a licensed installer can help ensure adherence to regulations.
Compliance guarantees safety and avoids legal complications.
Magnetic Lock Push-to-Exit Button Wiring Diagram
If you're setting up a maglock system, you'll likely need a push-to-exit button as part of the installation.
These buttons ensure a safe and user-friendly exit option. At our store, we sell complete kits that include a maglock, exit button, and power supply to make your installation easier.
Below, we will show an example diagram from one of those kits.

For more details, explore our recommended kits here:

Kit with Indoor Maglock and Waterproof Exit Button
(Model FPC-7311)

Kit with Indoor Maglock Lock and No Touch With Delay Push To Exit Button
(Model FPC-7312) Kit with Indoor Maglock Lock, Bracket and Green LED Push To Exit Button
Kit with Indoor Maglock Lock, Bracket and Green LED Push To Exit Button
(Model FPC-7313)
These kits are designed to provide everything you need in one package, simplifying the setup process and ensuring compatibility.
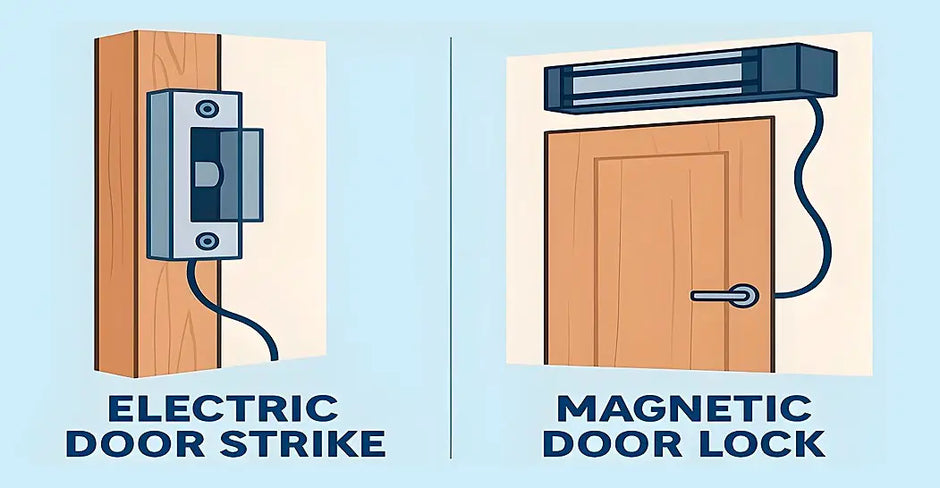
Magnetic Lock vs. Electric Strike

When comparing electromagnetic locks to electric strikes, it’s essential to consider your specific security needs and their fail-safe or fail-secure configurations:
Electromagnetic Lock (Maglock)
These are typically fail-safe devices, meaning they require constant power to remain locked. In the event of a power outage, the lock will disengage, allowing the door to open for safety. This makes them ideal for high-traffic areas or emergency exits.
Electric Strike
Electric strikes can be configured as either fail-safe or fail-secure. In a fail-secure setup, the door remains locked during a power outage, ensuring security. This configuration is commonly used for applications where maintaining security during power loss is critical.
Both options have their pros and cons, and the right choice depends on the balance between safety and security in your specific application.
It’s worth consulting with a security expert to determine the best fit for your needs.
Integrating Electromagnetic Locks with Access Control Systems

Electromagnetic locks are commonly used in modern access control systems to enhance security and streamline entry management. These systems allow users to control who can enter and exit a property by integrating electromagnetic door locks with devices such as:
Keycards or Fobs: Users can unlock doors by presenting authorized credentials.
Biometric Scanners: Fingerprint or facial recognition systems can trigger the lock to disengage for authorized individuals.
PIN Keypads: A user inputs a unique code to gain access.
Remote Monitoring: Security personnel can manage locks and monitor access points remotely through software or networked control systems.
By combining maglocks with these access control elements, property managers can create a layered security approach.
These setups are particularly beneficial in commercial environments, multi-unit residential buildings, and high-security areas. For hidden doors in private rooms or secret compartments, maglocks provide a reliable and invisible locking option, blending functionality with aesthetics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What’s the typical holding force of a magnetic lock?
VISIONIS models range from 300 to 1,200 pounds, depending on the model. Higher force means stronger security.
2. Can magnetic locks be used outdoors?
Yes, but you’ll need a weatherproof model designed for harsh conditions.
3. How do I integrate a maglock with my access control system?
Maglocks work seamlessly with keypads, card readers, and biometric scanners. They’re also great for remote management systems.
4. What happens during a power outage?
Most electromagnetic door locks unlock automatically (fail-safe). To maintain security, consider a UPS or battery backup.
5. Is professional installation necessary?
Not always. DIYers can handle most installations with the right tools and instructions. That said, complex setups may require a professional touch.
6. How do I troubleshoot a malfunctioning maglock?
Check for misalignment, wiring errors, or power supply issues. Regular maintenance can prevent most problems.
7. Where can I buy a maglock kit?
We offer complete magnetic locks kits that include the lock, power supply, and exit button.
Conclusion
Electromagnetic locks are versatile, secure, and perfect for modern access control needs. Whether you’re outfitting an office, securing your home, or upgrading your building’s entry systems, a maglock is an excellent choice.
Need help picking the right one? Contact us today—we’re here to guide you every step of the way.